모든 HDLBits 포스팅은 Ligth Theme을 권장합니다.
(왼쪽 메뉴 하단)
문제는 반드시 HDLBits를 참고하세요! 보다 자세하게 적혀있습니다.
https://hdlbits.01xz.net/wiki/Exams/m2014_q4h
Exams/m2014 q4h - HDLBits
hdlbits.01xz.net
Basic Gates
Wire

Implement the following circuit.
주어진 회로를 구현하세요.
Solution ↓
module top_module (
input in,
output out);
assign out = in;
endmodule
GND

Implement the following circuit.
주어진 회로를 구현하세요.
Solution ↓
module top_module (
output out);
assign out = 1'b0;
endmodule
NOR

Implement the following circuit.
주어진 회로를 구현하세요.
Solution ↓
module top_module (
input in1,
input in2,
output out);
assign out = ~(in1 | in2);
endmodule
Another Gate

Implement the following circuit.
주어진 회로를 구현하세요.
Solution ↓
module top_module (
input in1,
input in2,
output out);
assign out = in1 & ~in2;
endmodule
Two Gates

Implement the following circuit.
주어진 회로를 구현하세요.
Solution ↓
module top_module (
input in1,
input in2,
input in3,
output out);
wire xnor2nor;
assign xnor2nor = ~(in1 ^ in2);
assign out = xnor2nor ^ in3;
endmodule
More Logic Gates
Ok, let's try building several logic gates at the same time. Build a combinational circuit with two inputs, a and b.
There are 7 outputs, each with a logic gate driving it:
- out_and: a and b
- out_or: a or b
- out_xor: a xor b
- out_nand: a nand b
- out_nor: a nor b
- out_xnor: a xnor b
- out_anotb: a and-not b
동시에 여러 Logic Gate를 만들어봅시다. 2개의 입력(a, b)으로 조합 회로를 구성하세요. 7개의 출력이 있고, 각각의 logic gate가 이를 구동합니다.
• out_and: a and b
• out_or: a or b
• out_xor: a xor b
• out_and: a nand b
• out_or: a nor b
• out_xor: a xnor b
• out_xor: a and-not b
Solution ↓
module top_module(
input a, b,
output out_and,
output out_or,
output out_xor,
output out_nand,
output out_nor,
output out_xnor,
output out_anotb
);
assign out_and = a & b;
assign out_or = a | b;
assign out_xor = a ^ b;
assign out_nand = ~(a & b);
assign out_nor = ~(a | b);
assign out_xnor = ~(a ^ b);
assign out_anotb = a & ~b;
endmodule
7420 Chip

The 7400-series integrated circuits are a series of digital chips with a few gates each. The 7420 is a chip with two 4-input NAND gates. Create a module with the same functionality as the 7420 chip. It has 8 inputs and 2 outputs
7400 시리즈 집적 회로는 각각 몇 개의 게이트가 있는 일련의 디지털 칩입니다. 7420은 2개의 4 입력 NAND 게이트가 있는 칩입니다.
7420 칩과 동일한 기능의 모듈을 제작합니다. 8개의 입력과 2개의 출력이 있습니다.
Solution ↓
module top_module (
input p1a, p1b, p1c, p1d,
output p1y,
input p2a, p2b, p2c, p2d,
output p2y );
assign p1y = ~(p1a & p1b & p1c & p1d);
assign p2y = ~(p2a & p2b & p2c & p2d);
endmodule
Truth Tables

| Row | Inputs | Outputs | ||
| Number | x3 x2 x1 | f | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Create a combinational circuit that implements the above truth table.
위의 진리표를 따르는 조합회로를 구성하세요.
Solution ↓
module top_module(
input x3,
input x2,
input x1, // three inputs
output f // one output
);
assign f = (~x1&x2&~x3) | (x1&x2&~x3) | (x1&~x2&x3) | (x1&x2&x3);
endmodule
Two-bit Equality
Create a circuit that has two 2-bit inputs A[1:0] and B[1:0], and produces an output z. The value of z should be 1 if A = B, otherwise z should be 0.
2개의 2-bit 입력 A[1:0]와 B[1:0]를 포함하고 z를 출력하는 회로를 만드세요. z는 A = B 이면 1이고, 아닐 때는 0이어야합니다.
Solution ↓
module top_module ( input [1:0] A, input [1:0] B, output z );
assign z = (A == B)? 1 : 0;
endmodule
Simple Circuit A
Module A is supposed to implement the function z = (x^y) & x. Implement this module.
모듈 A는 z = ( x ^ y ) & x를 구현하도록 되어있습니다. 이 모듈을 구현해요.
Solution ↓
module top_module (input x, input y, output z);
assign z = (x^y) & x;
endmodule
Simple Circuit B

Circuit B can be described by the following simulation waveform. Implement this circuit.
회로 B는 주어진 시뮬레이션 파형을 보여줍니다. 이 회로를 구현하세요.
Solution ↓
module top_module ( input x, input y, output z );
assign z = ~(x^y);
endmodule
Combine Circuits A and B

Implement the following circuit.
주어진 회로를 구현하세요.
Solution ↓
module top_module (input x, input y, output z);
wire out_a1,
out_a2,
out_b1,
out_b2,
or_ab,
and_ab;
assign out_a1 = (x ^ y) & x;
assign out_a2 = (x ^ y) & x;
assign out_b1 = ~(x ^ y);
assign out_b2 = ~(x ^ y);
assign or_ab = out_a1 | out_b1;
assign and_ab = out_a1 & out_b2;
assign z = or_ab ^ and_ab;
endmodule
Ring or Vibrate?
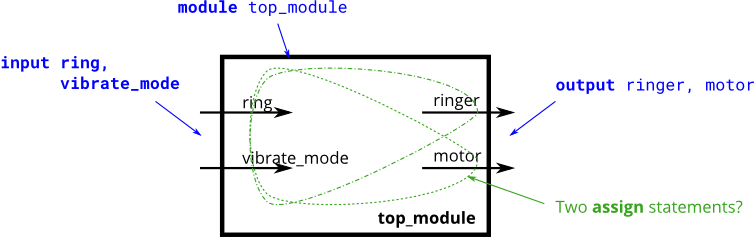
Suppose you are designing a circuit to control a cellphone's ringer and vibration motor. Whenever the phone needs to ring from an incoming call (input ring), your circuit must either turn on the ringer (output ringer = 1) or the motor (output motor = 1), but not both. If the phone is in vibrate mode (input vibrate_mode = 1), turn on the motor. Otherwise, turn on the ringer.
휴대폰의 벨소리와 진동 모터를 제어하기 위한 회로를 설계 중이라고 가정해 보겠습니다. 전화기가 수신 전화(input ring)로부터 울려야 할 때마다 회로는 벨소리(output ringer = 1) 또는 모터(output moter= 1)를 켜야 하지만 둘 다 켜지는 않습니다. 전화기가 진동 모드(input vibrate_mode = 1)에 있으면 모터를 켜십시오. 그렇지 않으면 링거를 켜십시오.
Solution ↓
module top_module (
input ring,
input vibrate_mode,
output ringer, // Make sound
output motor // Vibrate
);
assign motor = vibrate_mode & ring;
assign ringer = ~vibrate_mode & ring;
endmodule
Thermostat
The thermostat can be in one of two modes: heating (mode = 1) and cooling (mode = 0). In heating mode, turn the heater on when it is too cold (too_cold = 1) but do not use the air conditioner. In cooling mode, turn the air conditioner on when it is too hot (too_hot = 1), but do not turn on the heater. When the heater or air conditioner are on, also turn on the fan to circulate the air. In addition, the user can also request the fan to turn on (fan_on = 1), even if the heater and air conditioner are off.
서모스탯은 heating(mode = 1)과 cooling(mode = 0) 두 가지 모드 중 하나가 될 수 있습니다. heating 모드에서는 너무 추울 때(too_cold = 1) 히터를 켜되 에어컨은 사용하지 마십시오. cooling 모드에서는 너무 더울 때(too_hot = 1) 에어컨을 켜되 히터는 켜지 마십시오. 히터 또는 에어컨이 켜져 있을 때도 팬을 켜 공기를 순환시킵니다. 또한 사용자는 히터 및 에어컨이 꺼져 있더라도 팬을 켜달라고 요청할 수 있습니다(fan_on = 1).
Solution ↓
module top_module (
input too_cold,
input too_hot,
input mode,
input fan_on,
output heater,
output aircon,
output fan
);
assign heater = mode & too_cold;
assign aircon = !mode & too_hot;
assign fan = heater | aircon | fan_on;
endmodule
3-bit Populatoin Count
A "population count" circuit counts the number of '1's in an input vector. Build a population count circuit for a 3-bit input vector.
"population count" 회로는 입력 벡터에 있는 '1'의 수를 세는 회로입니다. 3-bit 입력 벡터에 대한 인구 수 회로를 만드세요.
Solution ↓
module top_module(
input [2:0] in,
output [1:0] out );
integer i;
always @ (*) begin
out = 2'b0;
for (i=0; i < 3; i++)begin
if(in[i])
out = out + 2'b1;
end
end
endmodule
Gates and Vectors
You are given a four-bit input vector in[3:0]. We want to know some relationships between each bit and its neighbour:
- out_both: Each bit of this output vector should indicate whether both the corresponding input bit and its neighbour to the left (higher index) are '1'. For example, out_both[2] should indicate if in[2] and in[3] are both 1. Since in[3] has no neighbour to the left, the answer is obvious so we don't need to know out_both[3].
- out_any: Each bit of this output vector should indicate whether any of the corresponding input bit and its neighbour to the right are '1'. For example, out_any[2] should indicate if either in[2] or in[1] are 1. Since in[0] has no neighbour to the right, the answer is obvious so we don't need to know out_any[0].
- out_different: Each bit of this output vector should indicate whether the corresponding input bit is different from its neighbour to the left. For example, out_different[2] should indicate if in[2] is different from in[3]. For this part, treat the vector as wrapping around, so in[3]'s neighbour to the left is in[0].
4-bit 입력 벡터 in[3:0]이 제공됩니다.
• out_both: 출력 벡터의 각 비트는 해당 입력 비트와 왼쪽에 있는 인접 비트가 모두 '1'인지 여부를 나타내야 합니다. 예를 들어 out_both[2]는 in[2]와 in[3]이 모두 1인지 여부를 나타내야 합니다. in[3]에는 왼쪽에 인접한 비트가 없으므로 답이 분명하므로 out_both[3]을 알 필요가 없습니다.
• out_any: 출력 벡터의 각 비트는 해당 입력 비트와 오른쪽 인접 비트 중 하나가 '1'인지를 표시해야 합니다. 예를 들어 out_any[2]는 [2] 또는 [1] 중 하나가 1인지를 표시해야 합니다. in[0]에는 오른쪽 인접 비트가 없으므로 답이 분명하므로 out_any[0]을 알 필요가 없습니다.
• out_different: 출력 벡터의 각 비트는 해당 입력 비트가 왼쪽의 이웃 비트와 다른지 여부를 나타내야 합니다. 예를 들어 out_different[2]는 in[2]가 in[3]과 다른지 여부를 나타내야 합니다. 이 부분의 경우 벡터를 감싸고 있으므로 in[3]의 왼쪽 이웃은 in[0]에 있습니다.
Solution ↓
module top_module(
input [3:0] in,
output [2:0] out_both,
output [3:1] out_any,
output [3:0] out_different
);
integer i;
always @(*)
begin
for(i=0; i<3; i++)
begin
out_both[i] = in[i] & in[i+1];
out_any[i+1] = in[i] | in[i+1];
out_different[i] = in[i] ^ in[i+1];
end
out_different[3] = in[3] ^ in[0];
end
endmodule
Even Longer Vectors
You are given a 100-bit input vector in[99:0]. We want to know some relationships between each bit and its neighbour:
- out_both: Each bit of this output vector should indicate whether both the corresponding input bit and its neighbour to the left are '1'. For example, out_both[98] should indicate if in[98] and in[99] are both 1. Since in[99] has no neighbour to the left, the answer is obvious so we don't need to know out_both[99].
- out_any: Each bit of this output vector should indicate whether any of the corresponding input bit and its neighbour to the right are '1'. For example, out_any[2] should indicate if either in[2] or in[1] are 1. Since in[0] has no neighbour to the right, the answer is obvious so we don't need to know out_any[0].
- out_different: Each bit of this output vector should indicate whether the corresponding input bit is different from its neighbour to the left. For example, out_different[98] should indicate if in[98] is different from in[99]. For this part, treat the vector as wrapping around, so in[99]'s neighbour to the left is in[0]
100-bit 입력 벡터 in[99:0]이 제공됩니다.
• out_both: 출력 벡터의 각 비트는 해당 입력 비트와 왼쪽 인접 비트가 모두 '1'인지 여부를 표시해야 합니다. 예를 들어 out_both[98]은 in[98]과 in[99]이 모두 1인지 여부를 표시해야 합니다. in[99]에는 왼쪽 인접 비트가 없으므로 답이 분명하므로 out_both[99]를 알 필요가 없습니다.
• out_any: 출력 벡터의 각 비트는 해당 입력 비트와 오른쪽 인접 비트 중 하나가 '1'인지를 표시해야 합니다. 예를 들어 out_any[2]는 [2] 또는 [1] 중 하나가 1인지를 표시해야 합니다. in[0]에는 오른쪽 인접 비트가 없으므로 답이 분명하므로 out_any[0]을 알 필요가 없습니다.
• out_different: 출력 벡터의 각 비트는 해당 입력 비트가 왼쪽의 이웃 비트와 다른지 여부를 나타내야 합니다. 예를 들어 out_different[98]은 in[98]이 in[99]와 다른지 여부를 나타내야 합니다. 이 부분의 경우 벡터를 감싸고 있으므로 in[99]의 왼쪽 이웃은 in[0]에 있습니다.
Solution ↓
module top_module(
input [99:0] in,
output [98:0] out_both,
output [99:1] out_any,
output [99:0] out_different
);
assign out_both = in[98:0] & in[99:1];
assign out_any = in[98:0] | in[99:1];
assign out_different = {(in[99] ^ in[0]), in[98:0] ^ in[99:1]};
endmodule
'Circuit Design > 🚀HDLBits' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [HDLBits] 8. Circuit - Combinational Logic (3) (0) | 2024.08.26 |
|---|---|
| [HDLBits] 7. Circuit - Combinational Logic (2) (1) | 2024.07.14 |
| [HDLBits] 5. Verilog Language - More Verilog Features (0) | 2024.07.11 |
| [HDLBits] 4. Verilog Language - Procedures (0) | 2024.07.08 |
| [HDLBits] 3. Verilog Language - Modules: Hiearch (0) | 2024.07.07 |
