모든 HDLBits 포스팅은 Ligth Theme을 권장합니다.
(왼쪽 메뉴 하단)
문제는 반드시 HDLBits를 참고하세요! 본 포스팅보다 자세하게 적혀있습니다.
https://hdlbits.01xz.net/wiki/Vector0
Vector0 - HDLBits
hdlbits.01xz.net
Vectors

Build a circuit that has one 3-bit input, then outputs the same vector, and also splits it into three separate 1-bit outputs. Connect output o0 to the input vector's position 0, o1 to position 1, etc.
3-Bit 입력이 1개인 회로를 만들고, 그다음에 동일한 vector를 출력하고, 또한 1-bit 출력을 3개로 분할합니다. 출력 o0를 입력 vector의 위치 0에 연결하고, o1을 위치 1 등에 연결합니다.
Solution ↓
module top_module (
input wire [2:0] vec,
output wire [2:0] outv,
output wire o2,
output wire o1,
output wire o0 ); // Module body starts after module declaration
assign outv = vec;
assign o0 = vec[0];
assign o1 = vec[1];
assign o2 = vec[2];
endmodule
Vectors in More Detail
Build a combinational circuit that splits an input half-word (16 bits, [15:0] ) into lower [7:0] and upper [15:8] bytes.
입력 Half-word (16-bit, [15:0])를 하위 [7:0] 및 상위 [15:8] byte로 분할하는 결합 회로를 구축합니다.
Solution ↓
`default_nettype none // Disable implicit nets. Reduces some types of bugs.
module top_module(
input wire [15:0] in,
output wire [7:0] out_hi,
output wire [7:0] out_lo );
assign out_lo = in [7:0];
assign out_hi = in [15:8];
endmodule
Vector Part Select
A 32-bit vector can be viewed as containing 4 bytes (bits [31:24], [23:16], etc.). Build a circuit that will reverse the byte ordering of the 4-byte word.
32-bit vector는 4byte(bit [31:24], [23:16] 등)를 포함하는 것으로 볼 수 있습니다. 4-byte 단어의 byte 순서를 반대로 되돌릴 회로를 구축합니다.
AaaaaaaaBbbbbbbbCcccccccDddddddd => DdddddddCcccccccBbbbbbbbAaaaaaaaSolution ↓
module top_module(
input [31:0] in,
output [31:0] out );//
assign out [31:24] = in [7:0];
assign out [23:16] = in [15:8];
assign out [15:8] = in [23:16];
assign out [7:0] = in [31:24];
// assign out[31:24] = ...;
endmodule
Bitwise Operators
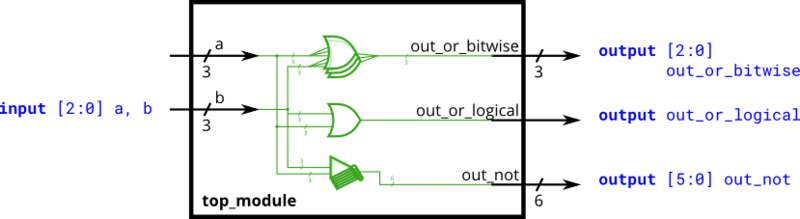
Build a circuit that has two 3-bit inputs that computes the bitwise-OR of the two vectors, the logical-OR of the two vectors, and the inverse (NOT) of both vectors. Place the inverse of b in the upper half of out_not (i.e., bits [5:3]), and the inverse of a in the lower half.
두 vector의 bitwise-OR, 두 vector의 논리-OR, 그리고 두 vector의 Inverter(NOT)를 계산하는 두 개의 3bit 입력이 있는 회로를 만드세요. 반전된 b를 out_not의 상위 절반에, 반전된 a를 하위 절반에 배치하세요.
Solution ↓
module top_module(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
output [2:0] out_or_bitwise,
output out_or_logical,
output [5:0] out_not
);
assign out_or_bitwise = a | b;
assign out_or_logical = a || b;
assign out_not [2:0] = ~ a [2:0];
assign out_not [5:3] = ~ b [2:0];
endmodule&&, & / |, || 의 차이 정확히 이해하기
& = Bit 연산자 (Bit 마다 대조)
&& = 논리 연산자 (전체 대조)
Four-input Gates
Build a combinational circuit with four inputs, in[3:0].
There are 3 outputs:
- out_and: output of a 4-input AND gate.
- out_or: output of a 4-input OR gate.
- out_xor: output of a 4-input XOR gate.
입력이 4개인 조합 회로를 [3:0]에 구축합니다.
3가지 출력:
• out_and: 4-입력 AND Gate의 출력.
• out_or: 4 입력 OR Gate의 출력.
• out_xor: 4 입력 XOR Gate의 출력.
Solution ↓
module top_module(
input [3:0] in,
output out_and,
output out_or,
output out_xor
);
assign out_and = in[0] && in[1] && in[2] && in[3];
assign out_or = in[0] || in[1] || in[2] || in[3];
assign out_xor = in[0] ^ in[1] ^ in[2] ^ in[3];
endmodule
Vector Concatenation Operator
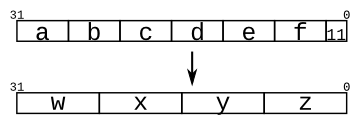
Given several input vectors, concatenate them together then split them up into several output vectors. There are six 5-bit input vectors: a, b, c, d, e, and f, for a total of 30 bits of input. There are four 8-bit output vectors: w, x, y, and z, for 32 bits of output. The output should be a concatenation of the input vectors followed by two 1 bits:
여러 개의 입력 vector가 주어졌을 때, 이들을 서로 연결한 다음 여러 개의 출력 vector로 나눕니다. 총 30bit의 입력을 위한 6개의 5-bit 입력 vector(a, b, c, d, e, f )와, 32bit의 출력을 위해서는 4개의 8-bit 출력 vector(w, x, y, z)가 있습니다. 출력은 입력 vector의 연결 다음에 1-bit 2개가 와야 합니다:
Solution ↓
module top_module (
input [4:0] a, b, c, d, e, f,
output [7:0] w, x, y, z );//
assign z = {e [0], f [4:0], 2'b11};
assign y = {d [3:0], e [4:1]};
assign x = {b [1:0], c [4:0], d[4]};
assign w = {a [4:0], b[4:2]};
// assign { ... } = { ... };
endmodule
Vector Reversal 1
Given an 8-bit input vector [7:0], reverse its bit ordering.
8-bit 입력 vector[7:0]가 주어지면 bit 순서를 반대로 바꿉니다.
Solution ↓
module top_module(
input [7:0] in,
output [7:0] out
);
assign out = {in[0], in[1], in[2], in[3], in[4], in[5], in[6], in[7]};
endmodule
Replication Operator
Build a circuit that sign-extends an 8-bit number to 32 bits. This requires a concatenation of 24 copies of the sign bit (i.e., replicate bit[7] 24 times) followed by the 8-bit number itself.
8-bit 수를 32-bit로 부호 확장하는 회로를 구축합니다. 이를 위해서는 부호 bit의 24개 복사본과 8-bit 수 자체를 24번 연결해야 합니다.
Solution ↓
module top_module (
input [7:0] in,
output [31:0] out );//
assign out = {{24 {in[7]}}, in[7:0]};
// assign out = { replicate-sign-bit , the-input };
endmodule
More Replication
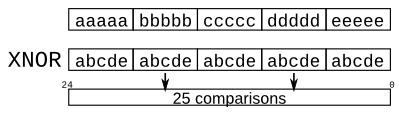
Given five 1-bit signals (a, b, c, d, and e), compute all 25 pairwise one-bit comparisons in the 25-bit output vector. The output should be 1 if the two bits being compared are equal.
5개의 1-bit 신호(a, b, c, d, e)가 주어지면 25bit 출력 vector에서 각각의 쌍별 1-bit 비교를 모두 계산합니다. 비교되는 두 bit가 같으면 출력은 1이어야 합니다.
out[24] = ~a ^ a; // a == a, so out[24] is always 1.
out[23] = ~a ^ b;
out[22] = ~a ^ c;
...
out[ 1] = ~e ^ d;
out[ 0] = ~e ^ e;Solution ↓
module top_module (
input a, b, c, d, e,
output [24:0] out );//
assign out = ~{{5{a}}, {5{b}}, {5{c}}, {5{d}}, {5{e}}} ^ {5{a,b,c,d,e}};
// The output is XNOR of two vectors created by
// concatenating and replicating the five inputs.
// assign out = ~{ ... } ^ { ... };
endmodule
'Circuit Design > 🚀HDLBits' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [HDLBits] 5. Verilog Language - More Verilog Features (0) | 2024.07.11 |
|---|---|
| [HDLBits] 4. Verilog Language - Procedures (0) | 2024.07.08 |
| [HDLBits] 3. Verilog Language - Modules: Hiearch (0) | 2024.07.07 |
| [HDLBits] 1. Verilog Language - Basics (0) | 2024.07.07 |
| [HDLBits] 0. Getting Started (0) | 2024.07.07 |

